Ship faster, safer, smarter. GitOps CI/CD with Tekton & ArgoCD - Part II
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
What is GitOps?
GitOps uses Git repositories as a single source of truth to deliver infrastructure as code. Submitted code checks the CI process, while the CD process checks and applies requirements for things like security, infrastructure as code, or any other boundaries set for the application framework. All changes to code are tracked, making updates easy while also providing version control should a rollback be needed.
GitOps delivers:
-
A standard workflow for application development
-
Increased security for setting application requirements upfront
-
Improved reliability with visibility and version control through Git
-
Consistency across any cluster, any cloud, and any on-premise environment Many other tools can be used together to build a GitOps framework. For example, git repositories, Kubernetes, continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) tools, and configuration management tools.
Understand GitOps
GitOps is a declarative way to implement continuous deployment for cloud native applications. You can use GitOps to create repeatable processes for managing OpenShift Container Platform clusters and applications across multi-cluster Kubernetes environments. GitOps handles and automates complex deployments at a fast pace, saving time during deployment and release cycles.
The GitOps workflow pushes an application through development, testing, staging, and production. GitOps either deploys a new application or updates an existing one, so you only need to update the repository; GitOps automates everything else.
GitOps is a set of practices that use Git pull requests to manage infrastructure and application configurations. In GitOps, the Git repository is the only source of truth for system and application configuration. This Git repository contains a declarative description of the infrastructure you need in your specified environment and contains an automated process to make your environment match the described state.
Also, it contains the entire state of the system so that the trail of changes to the system state are visible and auditable. By using GitOps, you resolve the issues of infrastructure and application configuration sprawl.
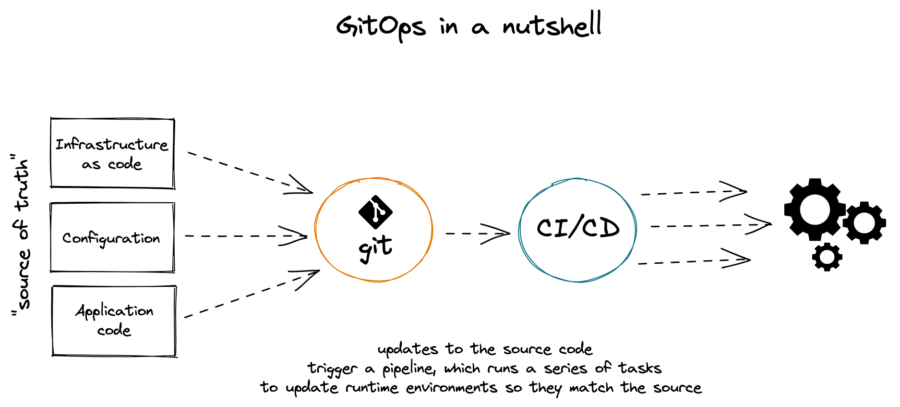
GitOps defines infrastructure and application definitions as code. Then, it uses this code to manage multiple workspaces and clusters to simplify the creation of infrastructure and application configurations.
By following the principles of the code, you can store the configuration of clusters and applications in Git repositories, and then follow the Git workflow to apply these repositories to your chosen clusters.
You can apply the core principles of developing and maintaining software in a Git repository to the creation and management of your cluster and application configuration files.
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps ensures consistency in applications when you deploy them to different clusters in different environments, such as: development, staging, and production. Red Hat OpenShift GitOps organizes the deployment process around the configuration repositories and makes them the central element. It always has at least two repositories:
-
Application repository with the source code
-
Environment configuration repository that defines the desired state of the application
These repositories contain a declarative description of the infrastructure you need in your specified environment. They also contain an automated process to make your environment match the described state.
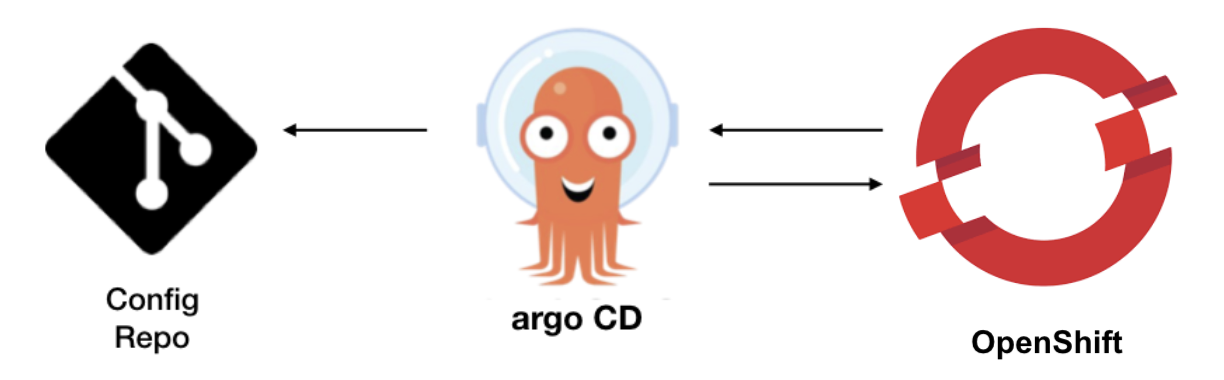
Red Hat OpenShift GitOps uses Argo CD to maintain cluster resources. Argo CD is an open-source declarative tool for the continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) of applications. Red Hat OpenShift GitOps implements Argo CD as a controller so that it continuously monitors application definitions and configurations defined in a Git repository. Then, Argo CD compares the specified state of these configurations with their live state on the cluster.
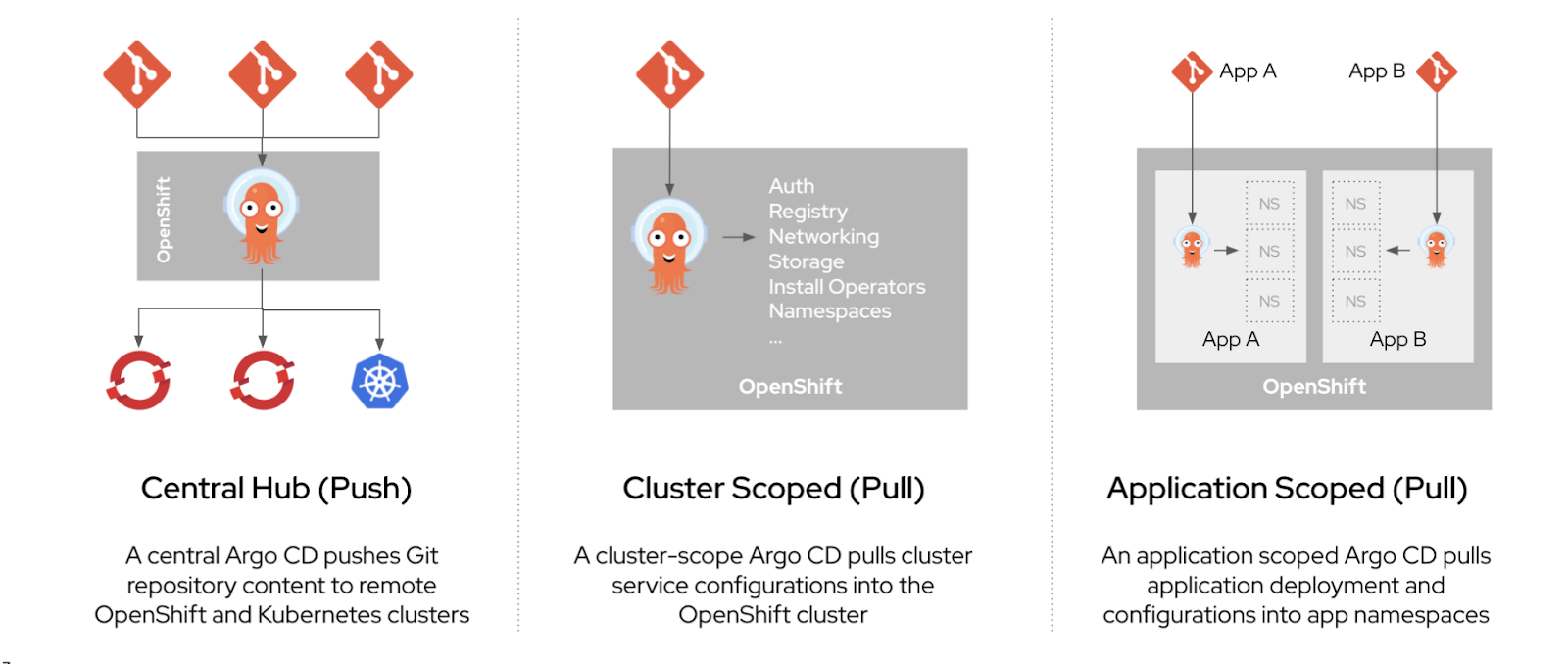
Argo CD reports any configurations that deviate from their specified state. These reports allow administrators to automatically or manually resync configurations to the defined state. Therefore, Argo CD enables you to deliver global custom resources, like the resources that are used to configure OpenShift Container Platform clusters.
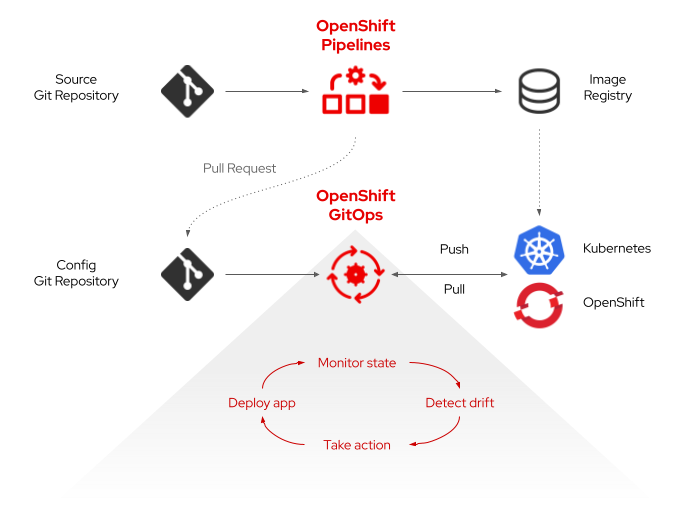
GitOps with Kustomize
What is Kustomize?
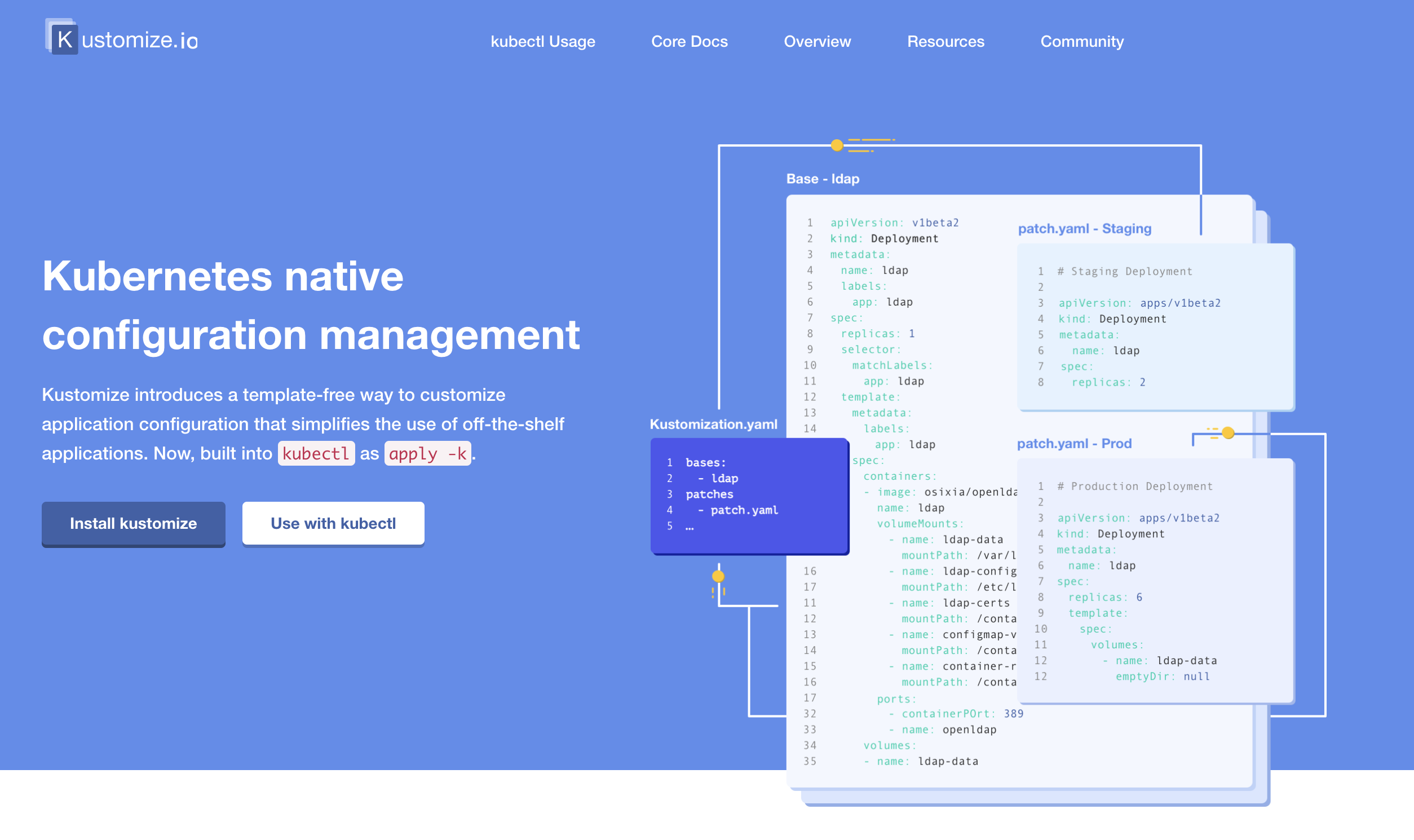
Kustomized provides a solution for customizing Kubernetes resource configuration free from templates and DSLs. Kustomize lets you customize raw, template-free YAML files for multiple purposes, leaving the original YAML untouched and usable as is.
Kustomize targets kubernetes; it understands and can patch kubernetes style API objects. It’s like make, in that what it does is declared in a file, and it’s like sed, in that it emits edited text.
With kustomize, your team can ingest any base file updates for your underlying components while keeping use-case specific customization overrides intact. Another benefit of utilizing patch overlays is that they add dimensionality to your configuration settings, which can be isolated for troubleshooting misconfigurations or layered to create a framework of most-broad to most-specific configuration specifications.
+ To recap, Kustomize relies on the following system of configuration management layering to achieve reusability:
-
Base Layer - Specifies the most common resources
-
Patch Layers - Specifies use case specific resources
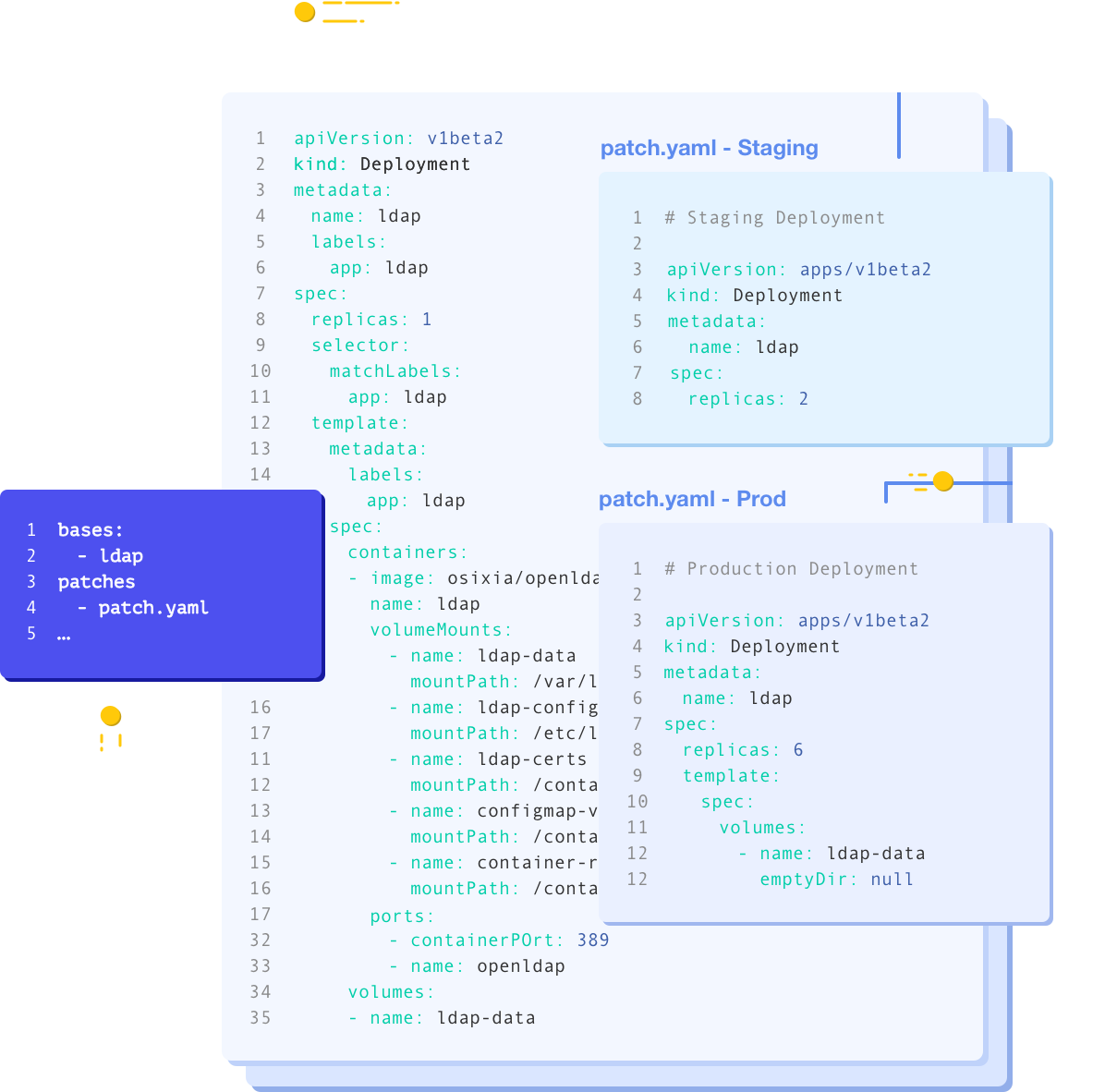
Kustomize Resources
-
For this workshop, we will deploy
simple-rest-goapplication agian using Red Hat OpenShift GitOps. -
Go to https://github.com/rhthsa/simple-rest-go to view application repository.
-
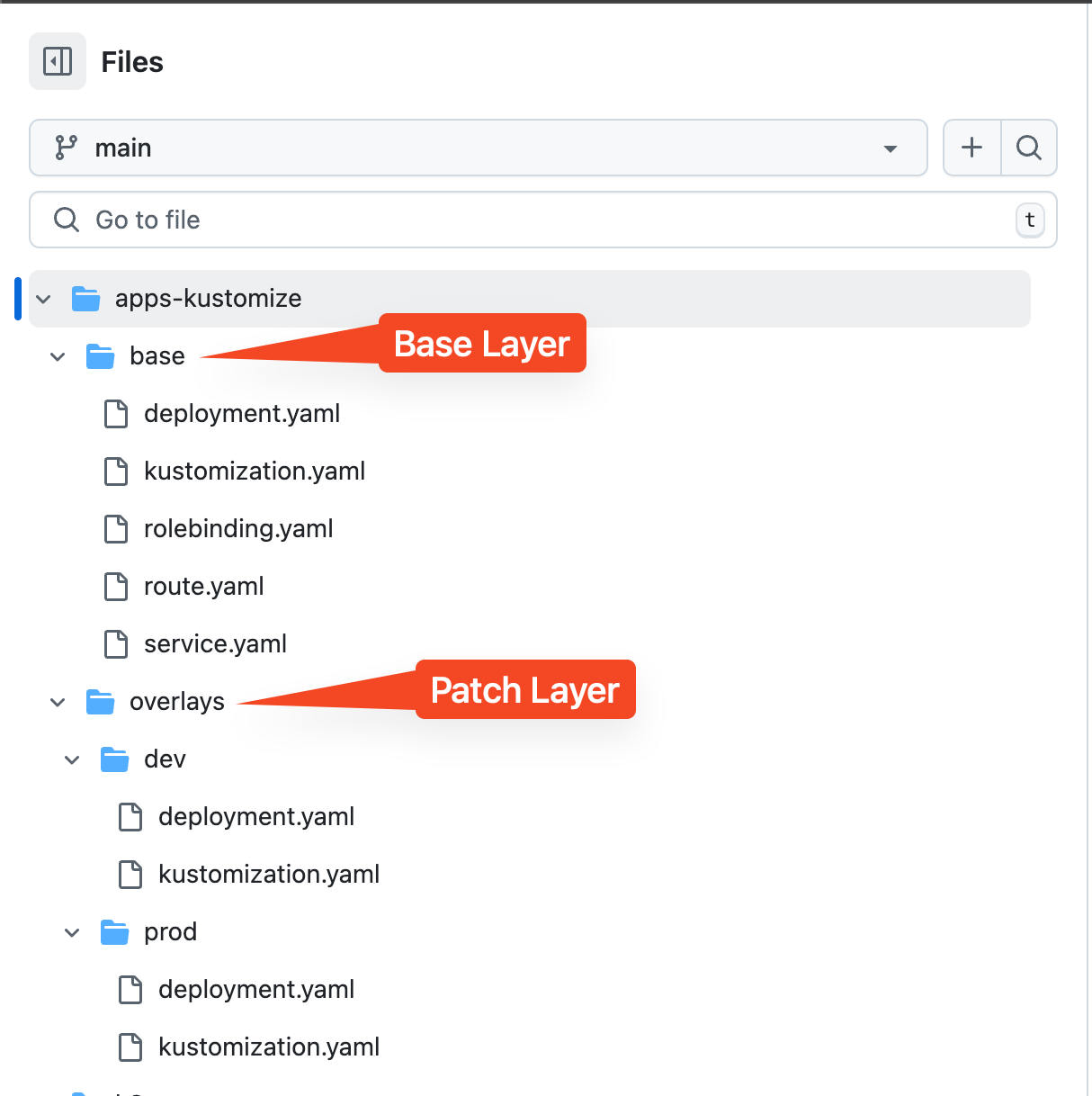
Go into apps-kustomize directory. There are 2 directoies, base directory contains all files for common resources, and overlays directory contains all use case or environment specific resources.
-
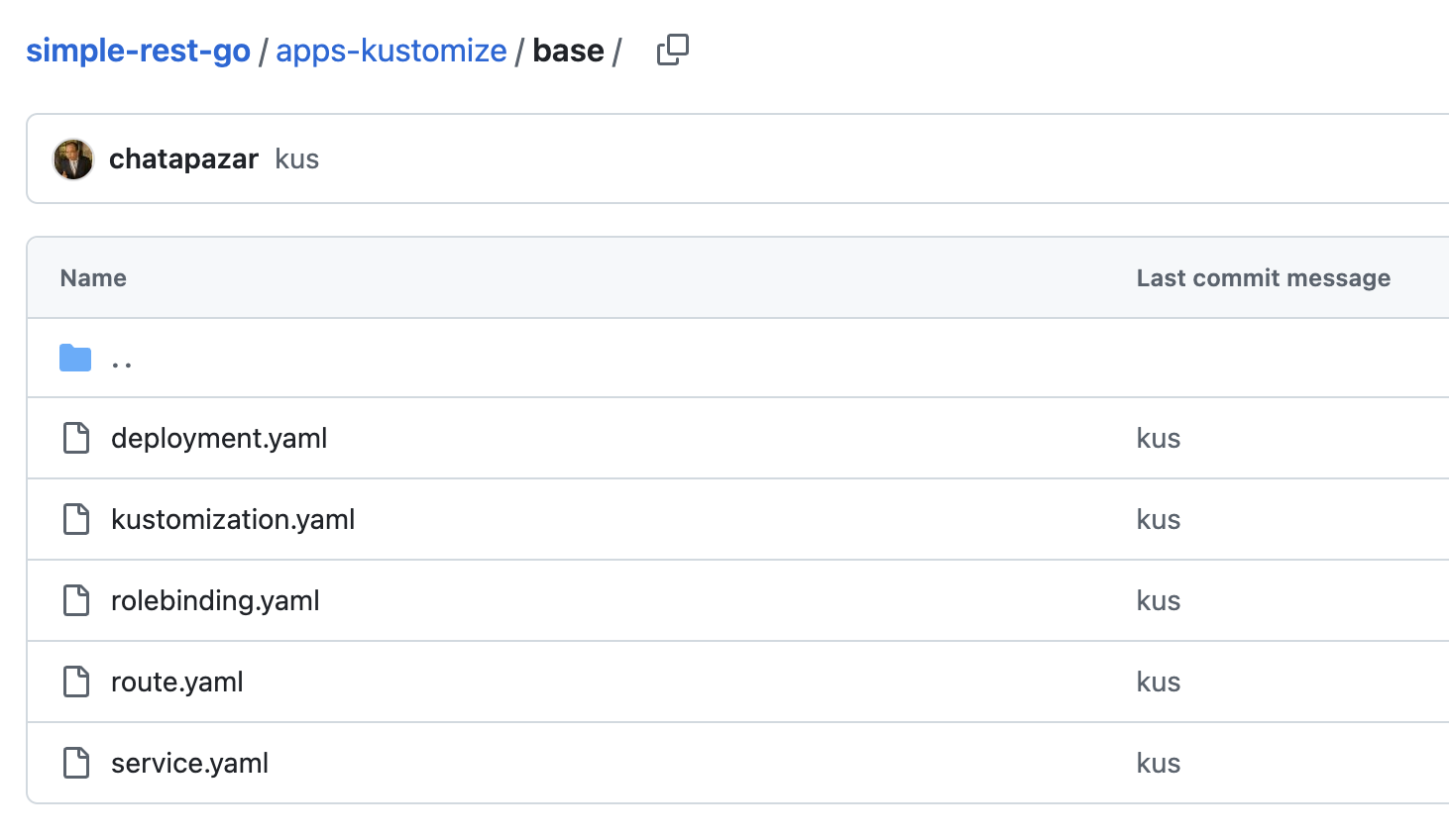
Go into the base directory.
-
Open these files to view configurations for application deployment (Configuration as Code). These files will be used as the base layer.
-
kustomization.yaml -
rolebinding.yaml -
deployment.yaml -
service.yaml -
route.yaml
-
-
-
Go to the overlays/dev directory. This directory contains configuration for the
Developmentenvironment.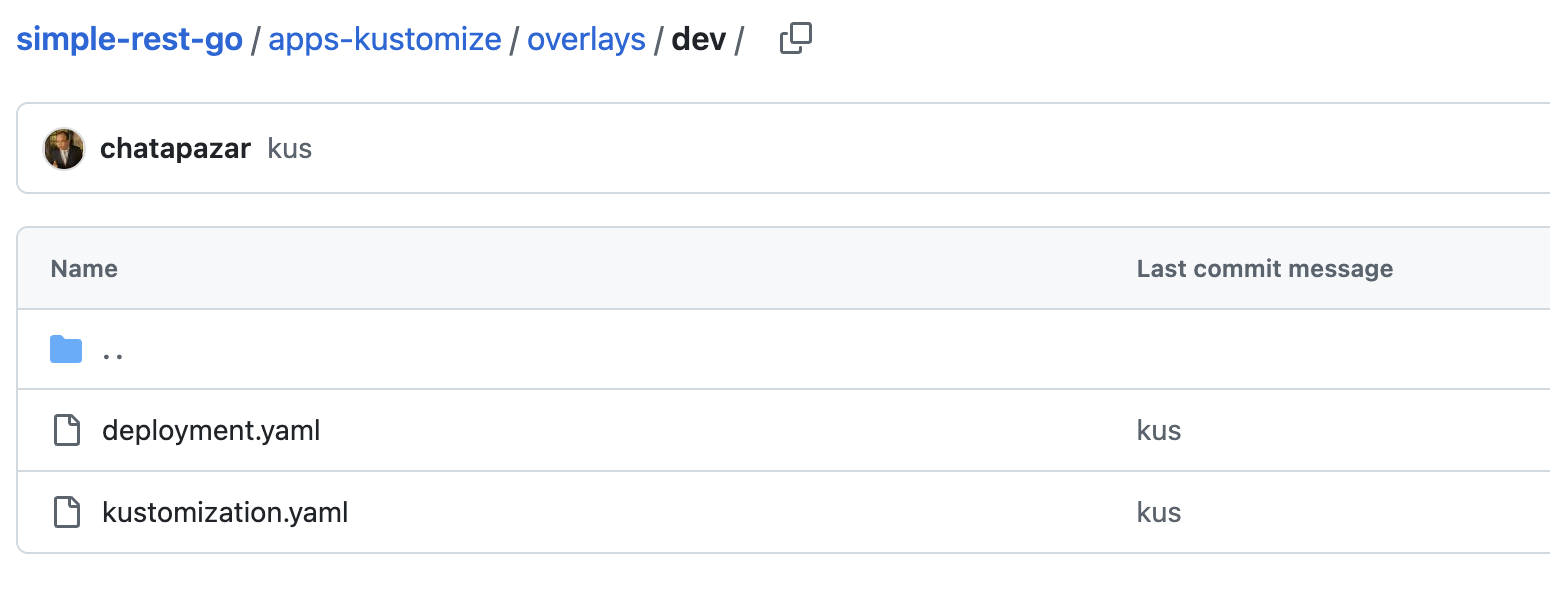
-
Review following files:
-
kustomization.yaml -
deployment.yaml
-
-
content of
deployment.yaml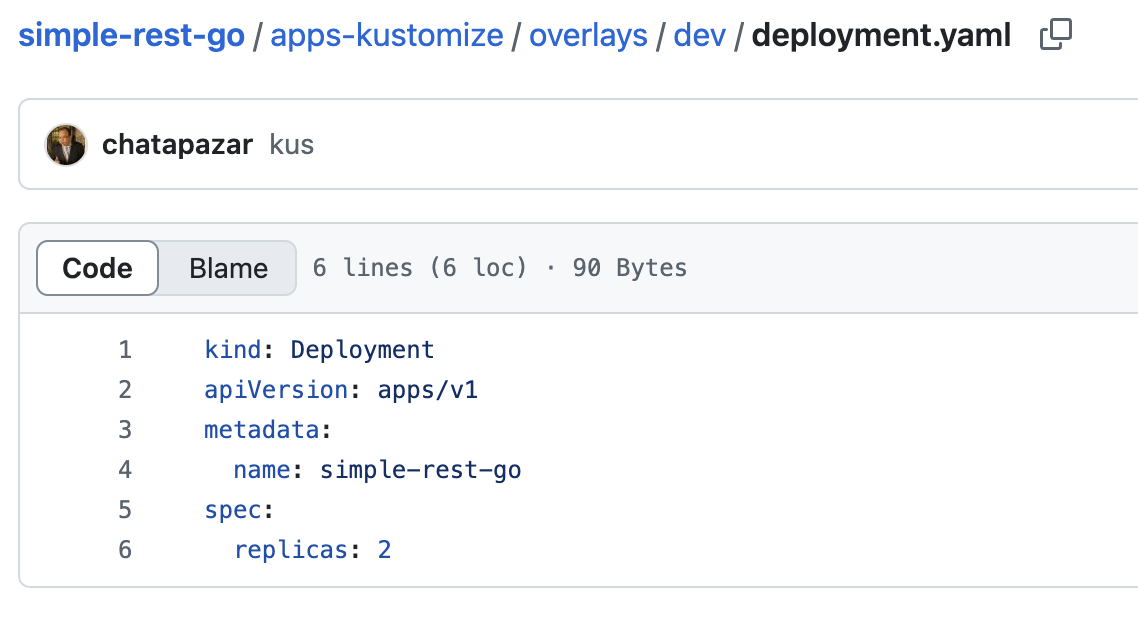
-
-
Go to the overlays/prod folder. This directory contains configuration for the
Productionenvironment.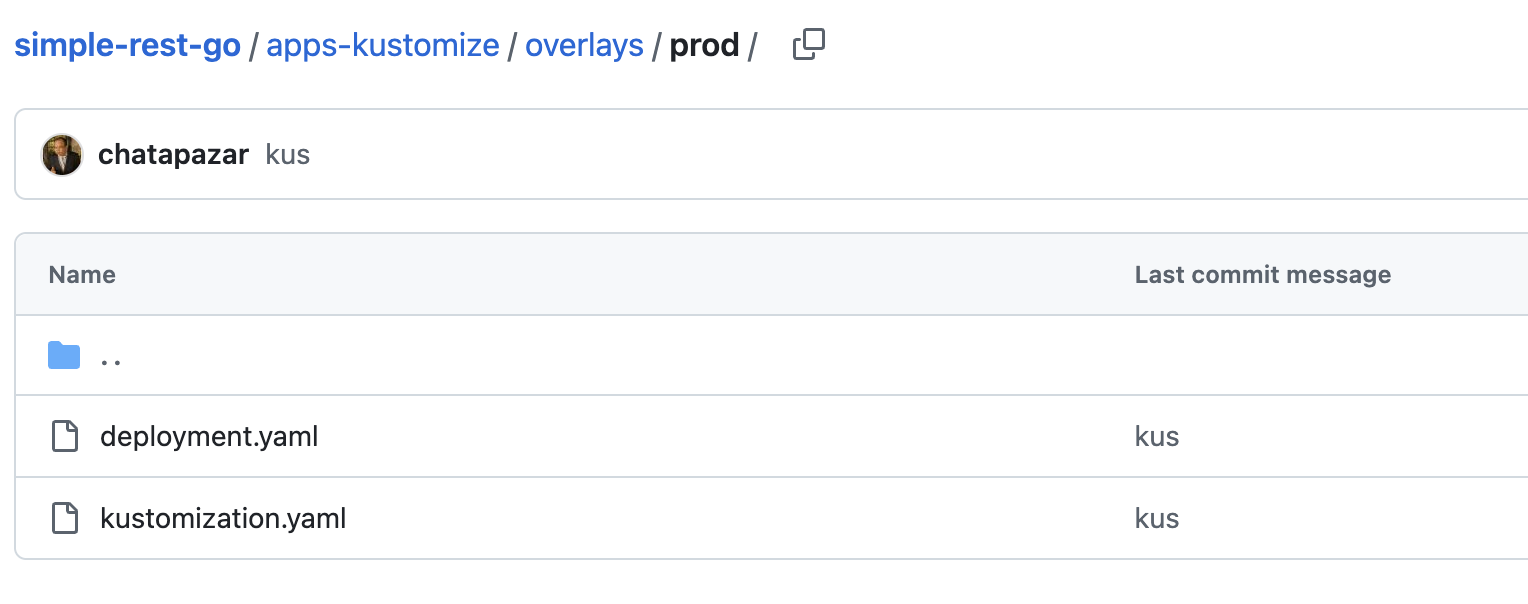
-
Review following file:
-
kustomization.yaml -
deployment.yaml
-
-
As you can see, the
replicasfield in thedeployment.yamlis3while the configuration for Development enviroyment (overlays/dev/deployment.yaml) is2.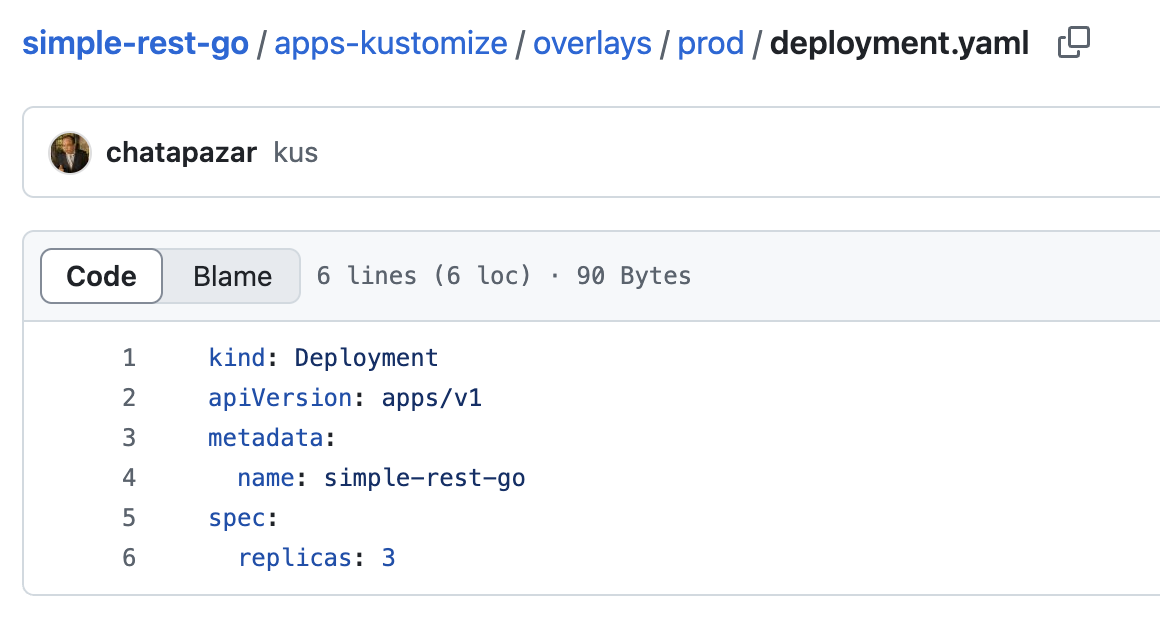
-
Deploy Applicaiton with OpenShift GitOps
In this lab we’re going to deploy the simple-rest-go application to OpenShift using OpenShift GitOps. The application will be deployed into 2 projects; userX-gitops-dev and userX-gitops-prod to pretend that you need to deploy the application to 2 environments - Development and Production respectively.
Let’s deploy the application for the Development environment first.
-
In OpenShift web console, click on the application palette icon at the top right corner then select OpenShift GitOps > Cluster Argo CD.
-
Log in with your username and password same as OpenShift’s credential.
-
On the Applications page, click + NEW APP button.
-
Enter
userX-go-devto Application Name (changeuserXto your username) -
Enter
defaultto Project Name -
Select
Manualfor SYNC POLICY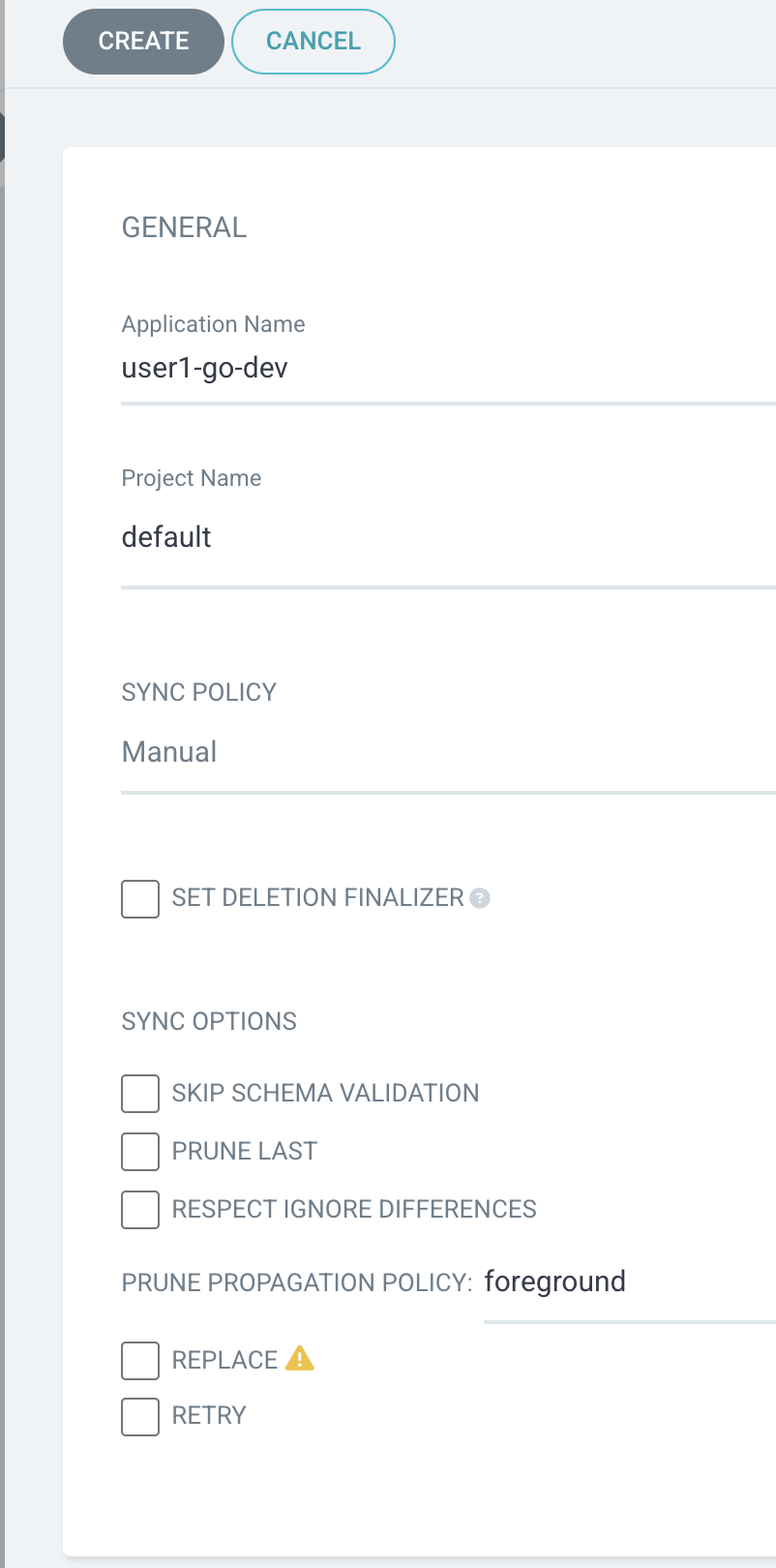
-
In the SOURCE section, enter
https://github.com/rhthsa/simple-rest-go.gitto Repository URL. -
Set Revision to
HEAD -
Enter
apps-kustomize/overlays/devto Path.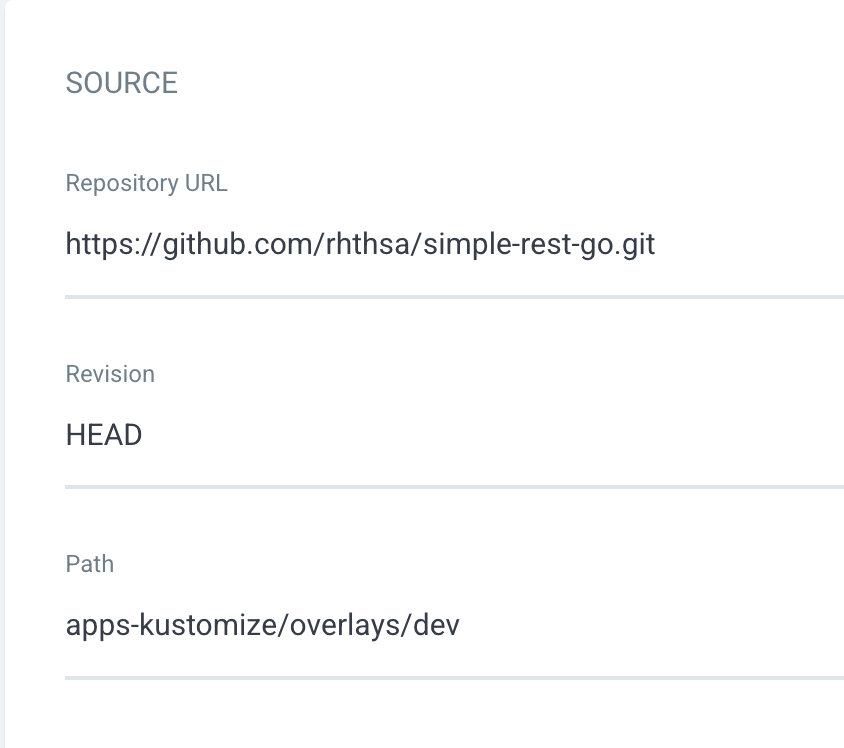
-
In the DESTINATION section, select the first cluster in Cluster URL dropdownlist.
-
Enter
userX-gitops-devto Namespace (changeuserX`to your username).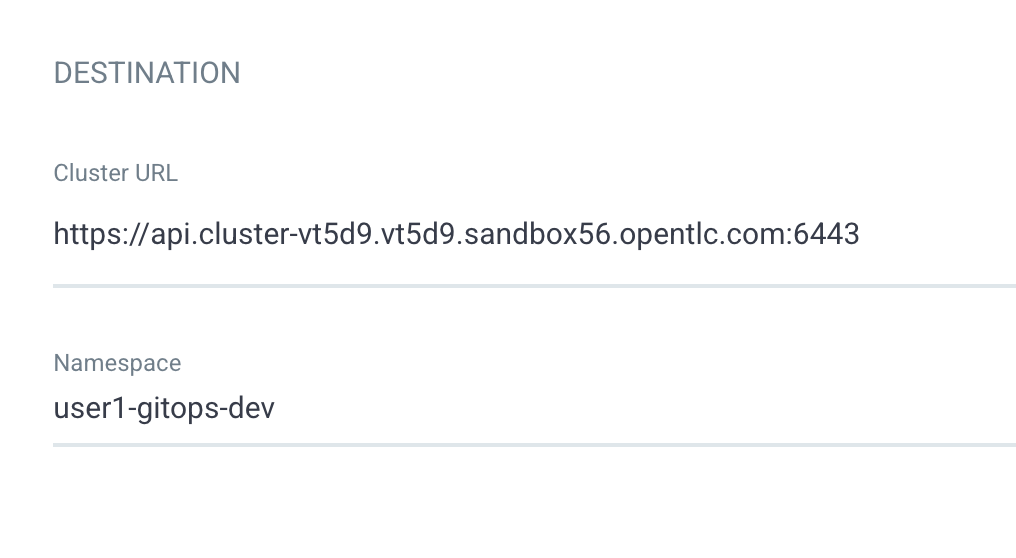
-
Leave default for the rest of configurations, then click Create button.
-
Back to the main page, set filter for NAMESPACES to
userX*(changeuserX`to your username), this helps filter only your app to be displayed on the page.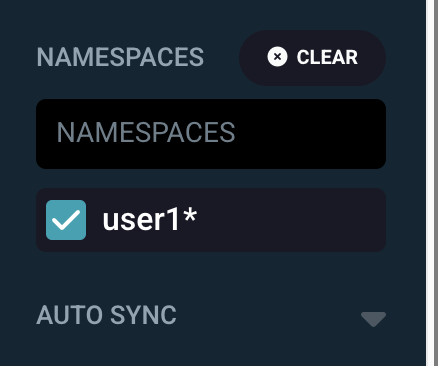
-
Review application in the Applications page, Click on
userX-go-devapplication tile to view application details.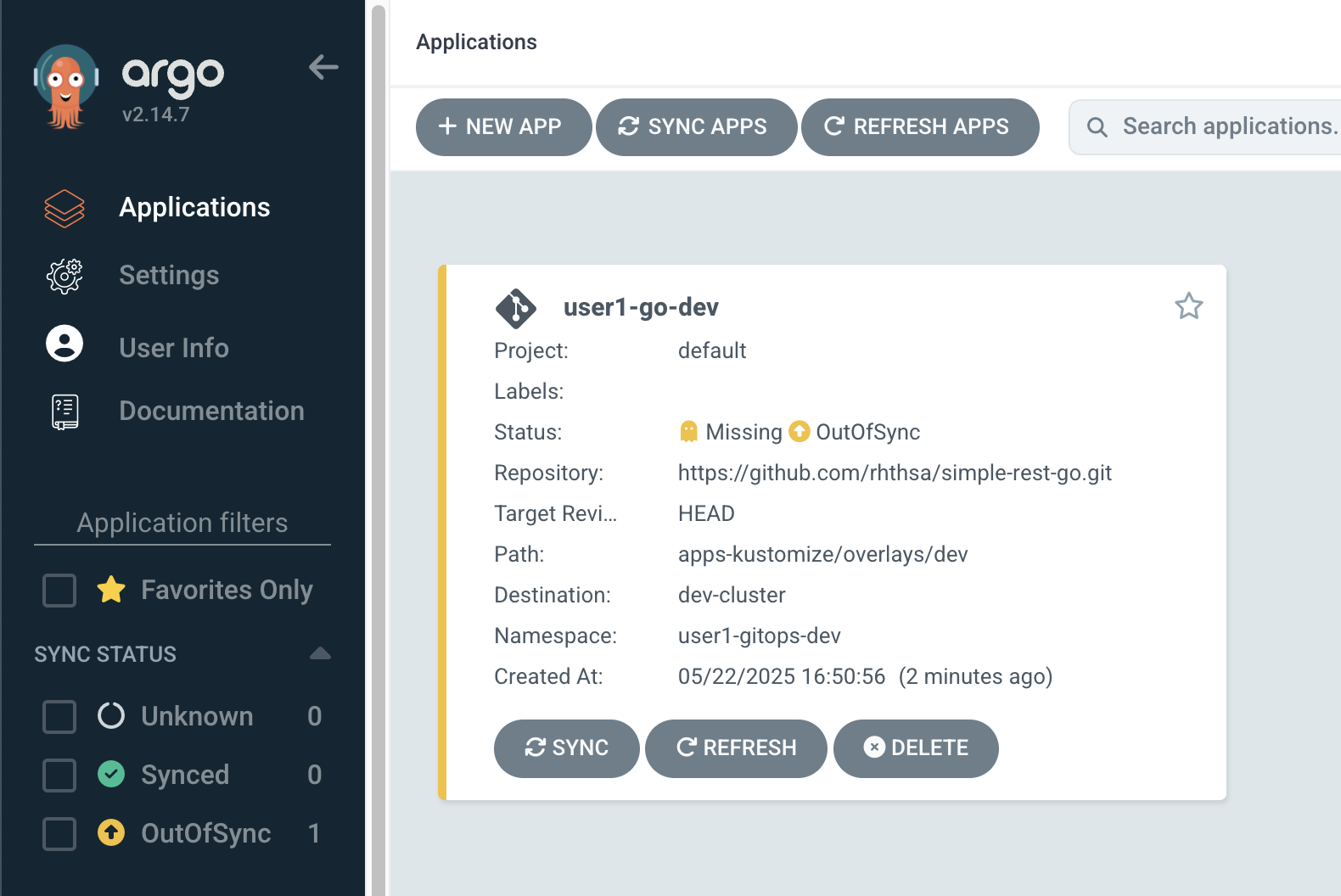
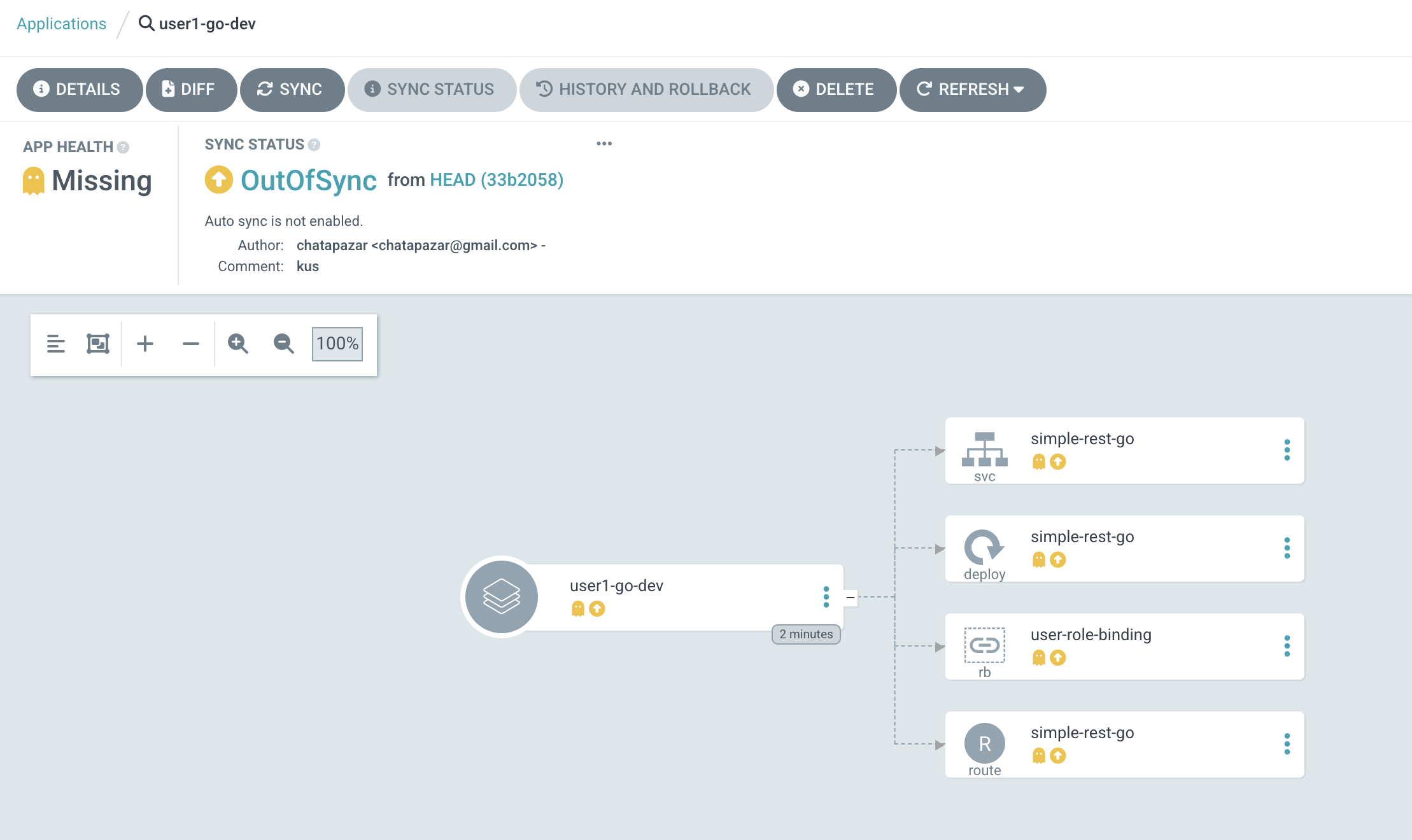
-
Click SYNC button then SYNCHRONIZE to synchronize application configurations from Git repository to your project on OpenShift.
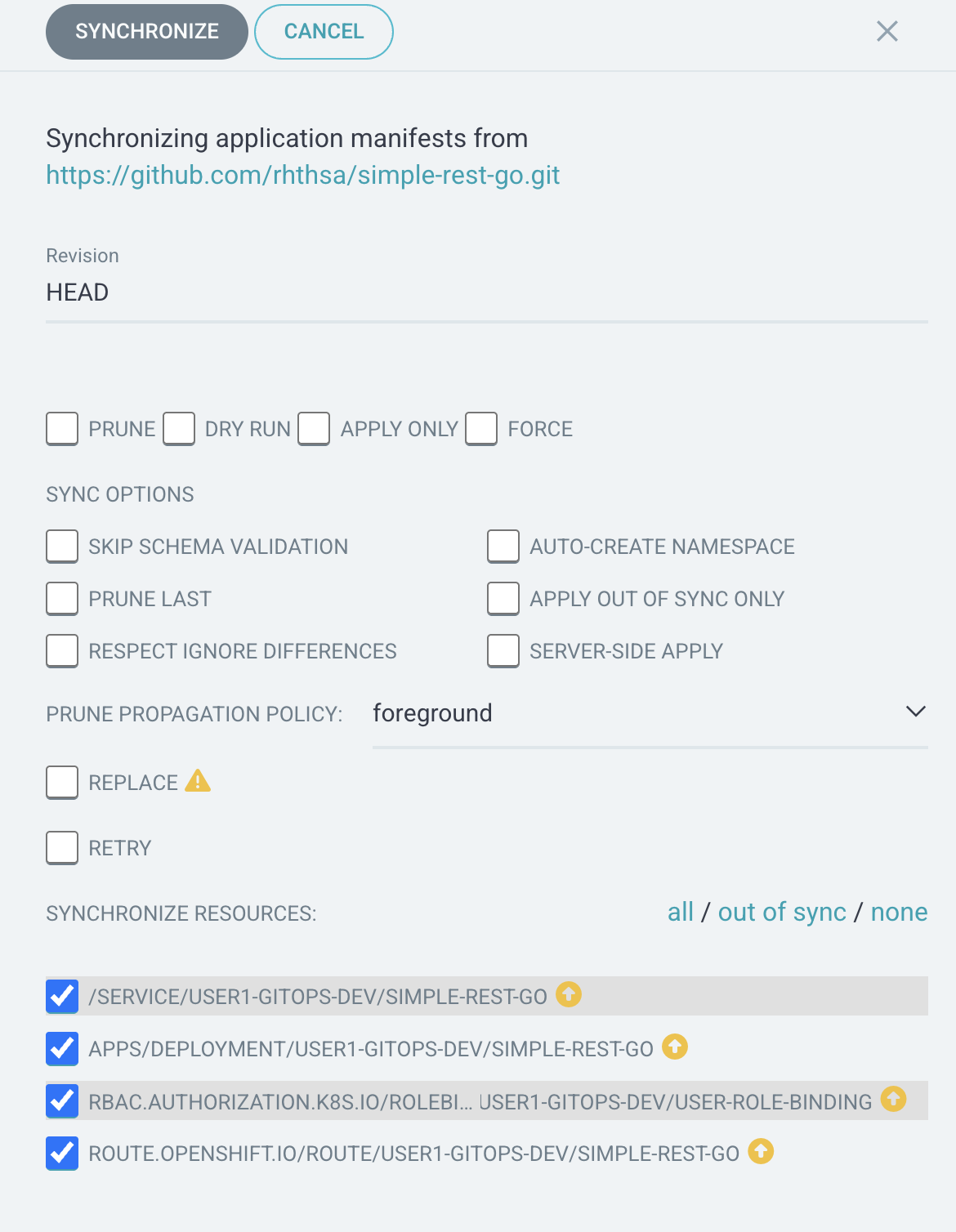
-
Wait until APP HEALTH status changed to
Healthy, SYNC STATUS changed toSynced, and LAST SYNC changed toSync OK. Then check number of pods, there should be 2 pods as configured in theoverlays/dev/deployment.yamlfile in Git repository you’ve reviewed before.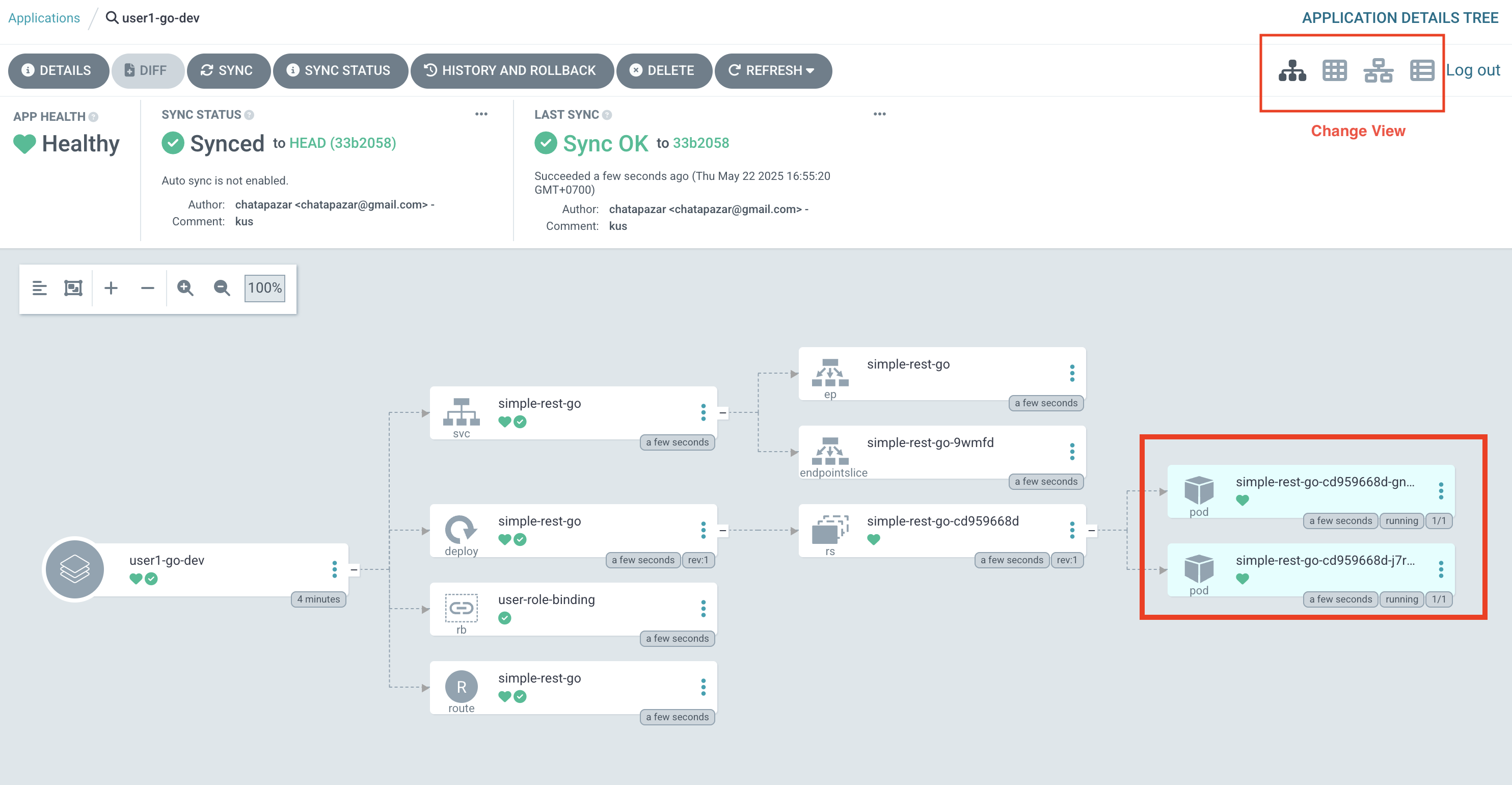
-
At the top right corner of application view area, you can change view mode to Tree view, Pods view, Network view, and List view to see resources in each view.
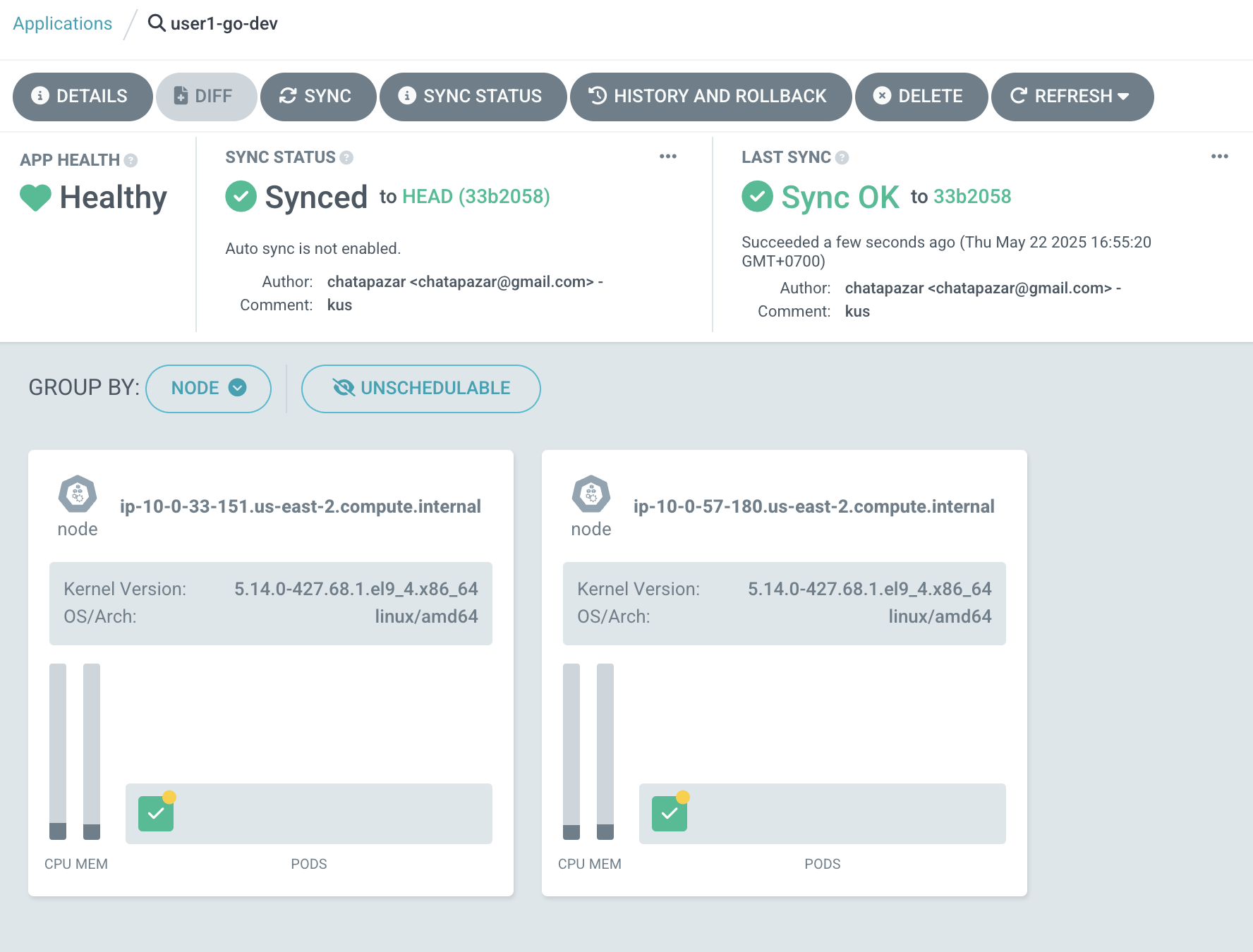
Sample of Pods view.
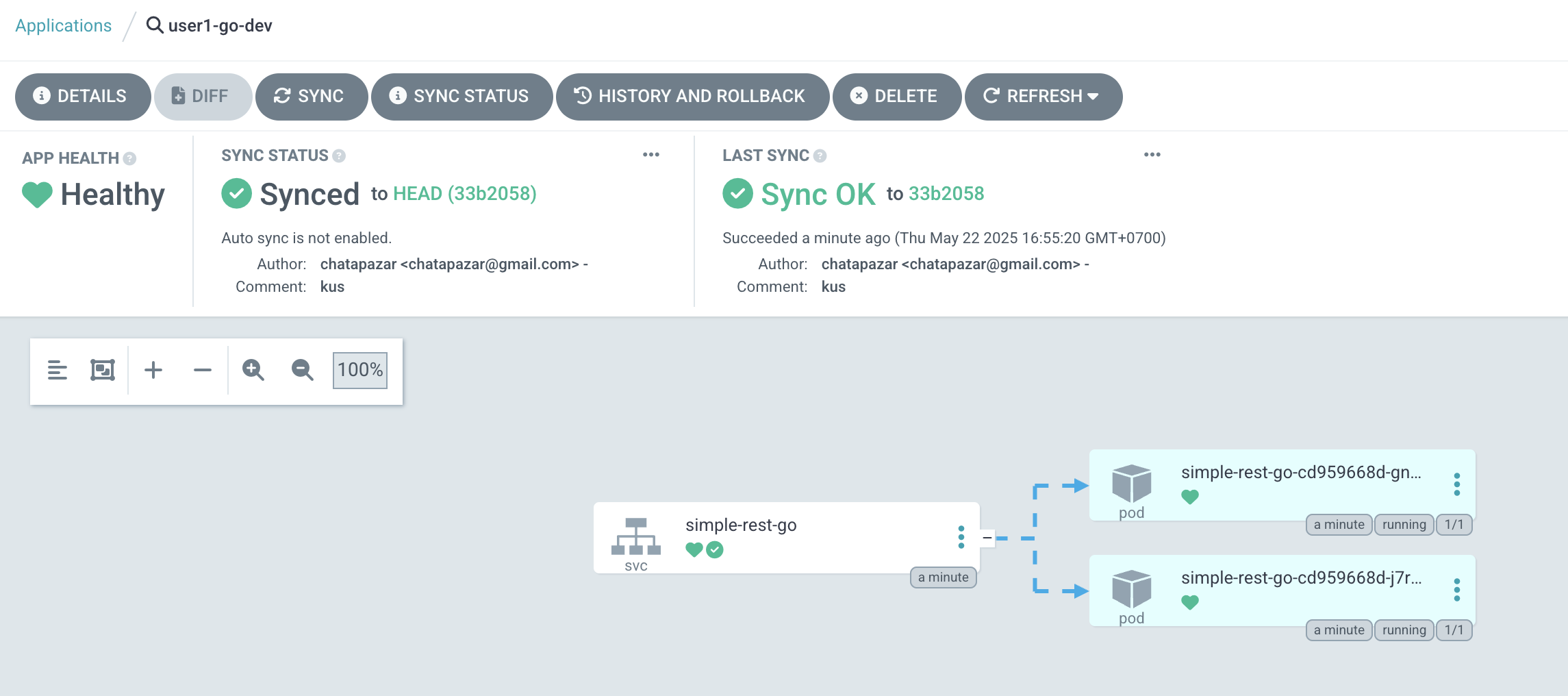
Sample of Network view.
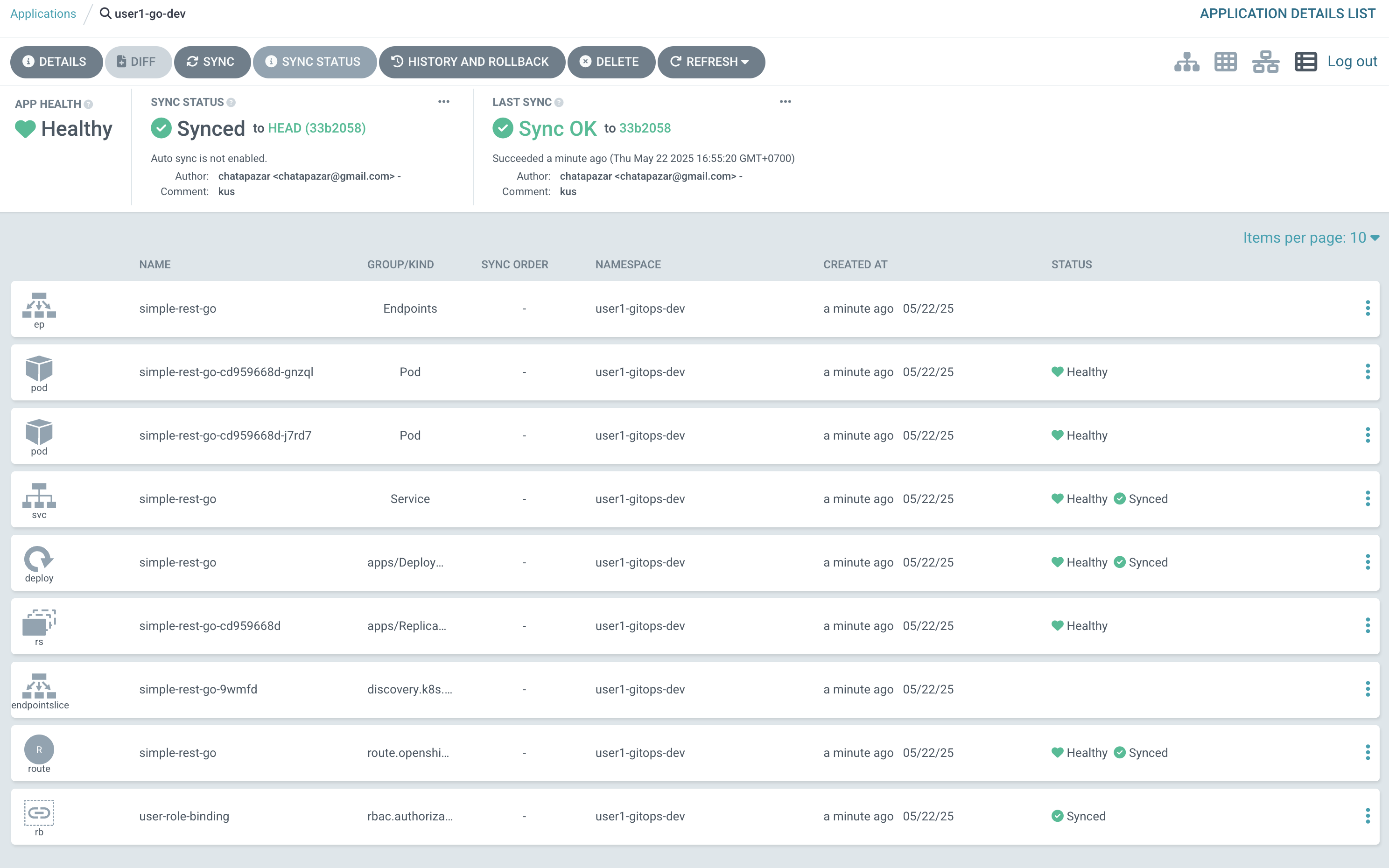
Sample of List view.
Next, let’s deploy the application for Production environment.
-
Select the Applications menu on the left, the click
+ NEW APPbutton. -
set Application Name to
userX-go-prod(changeuserXto your username) -
set Project Name to
default -
set SYNC POLICY to
Manual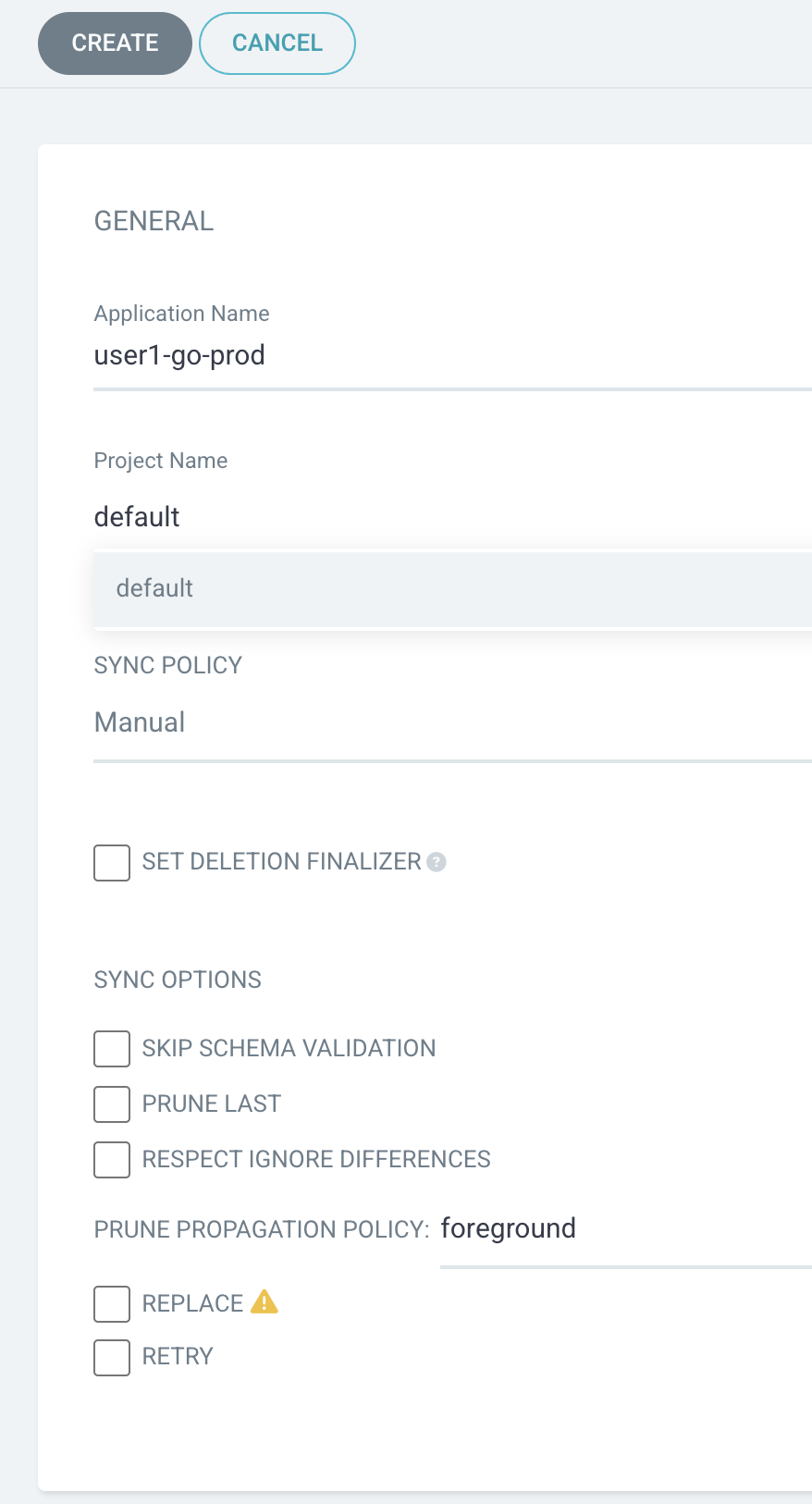
-
In the SOURCE section, Enter
https://github.com/rhthsa/simple-rest-go.gitto Repository URL. -
set Revision to
HEAD -
set Path to
apps-kustomize/overlays/prod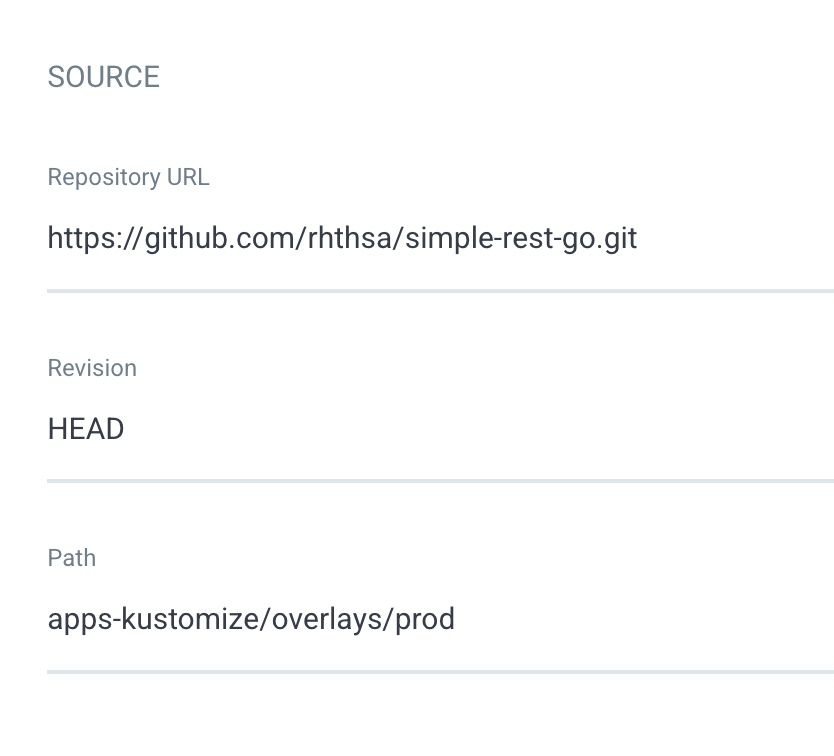
-
In the Destination section, select the first cluster in Cluster URL dropdownlist.
-
set Namespace to
userX-gitops-prod(changeuserX`to your username).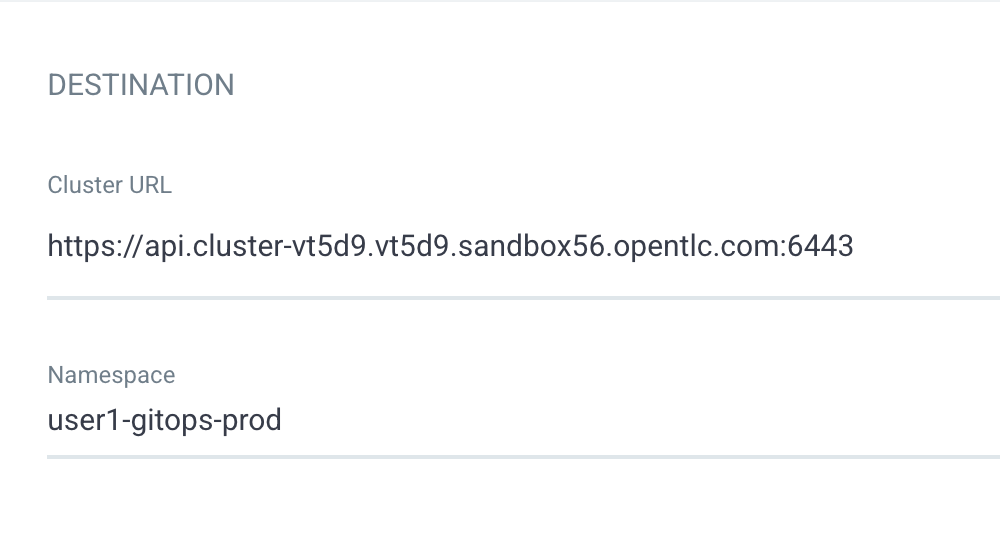
-
Leave default for the rest of configurations, then click Create button.
-
You should see a new application -
userX-go-prodthat matches to your username shows up. Click on in to see application details.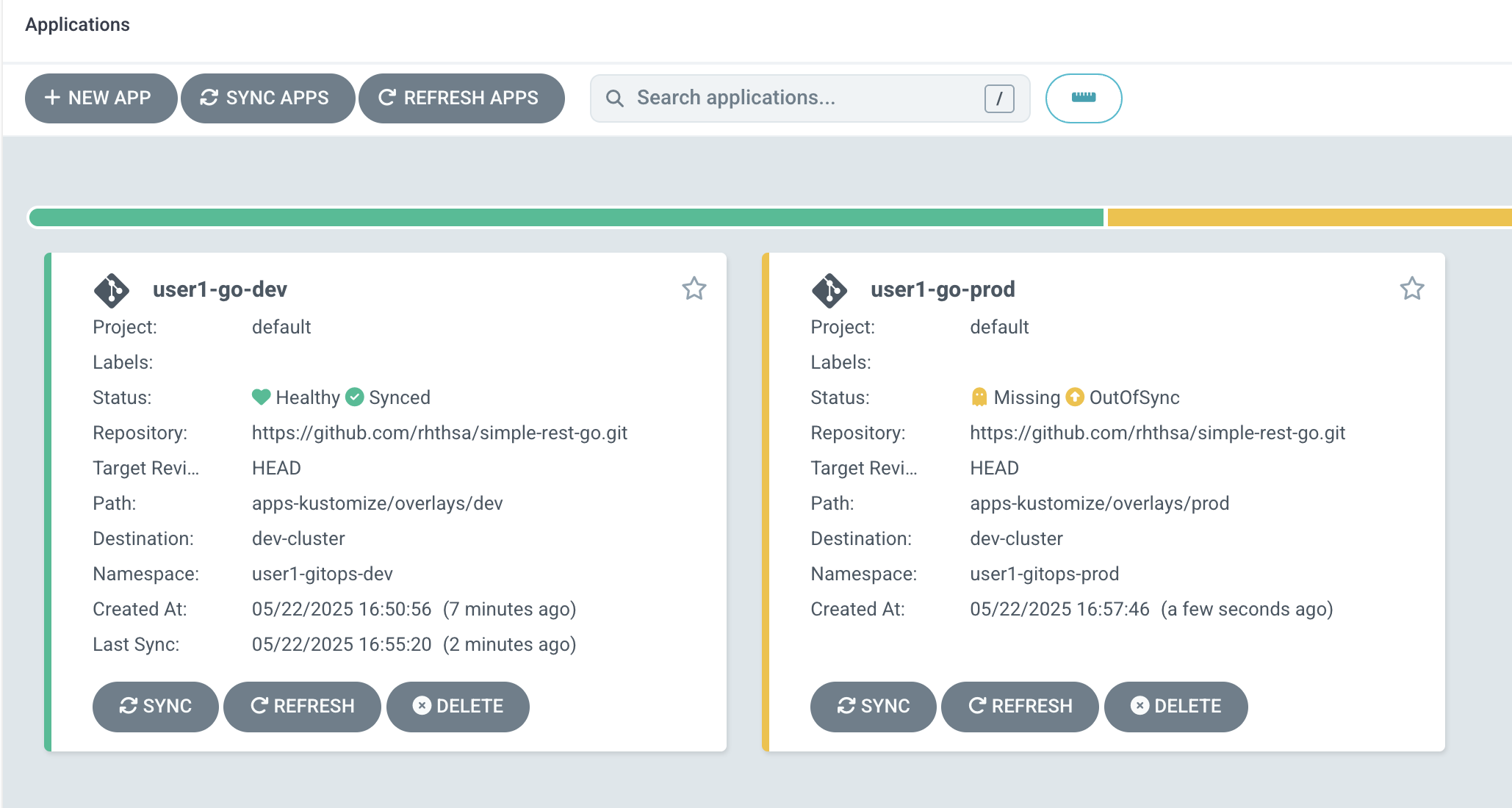
-
Click on SYNC to synchronize configurations from Git repository to OpenShift and wait until the synchonization completed, there should be 3 Pods running.
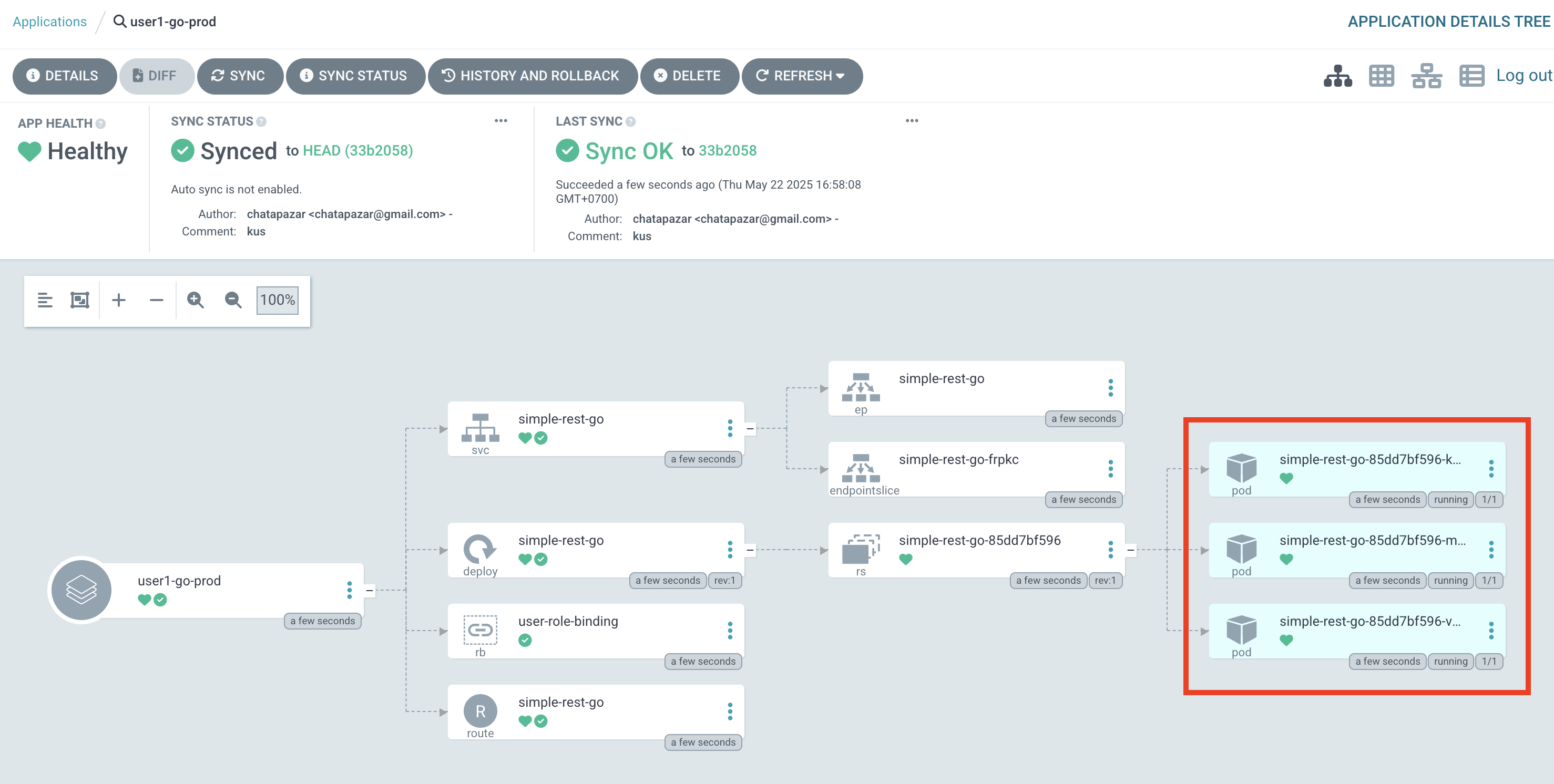
-
Go back to OpenShift Console, select Topology menu on the left. Change project to
userX-gitops-devmatches to your username, then click on thesimple-rest-goDeployment. On the right panel, click on Resources tab then check the number of Pods. There should be 2 Pods running.
-
Now change project to
userX-gitops-prodmatches to your username, then check the number of Pods. There should be 3 Pods running.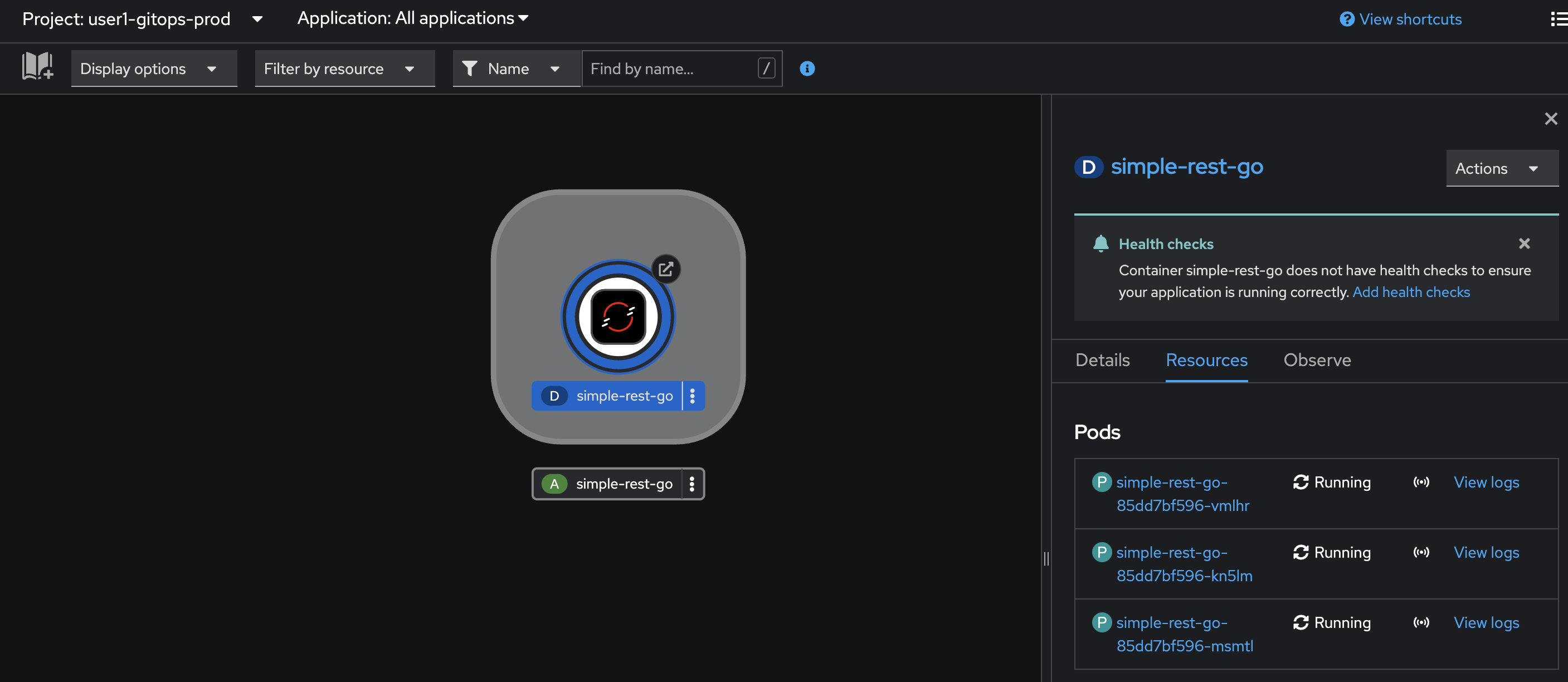
-
In the
userX-gitops-prodproject, try to reduce the number of replicas by just go to the Details tab on the right panel, click on v to scale down the application from 3 to 2 replicas.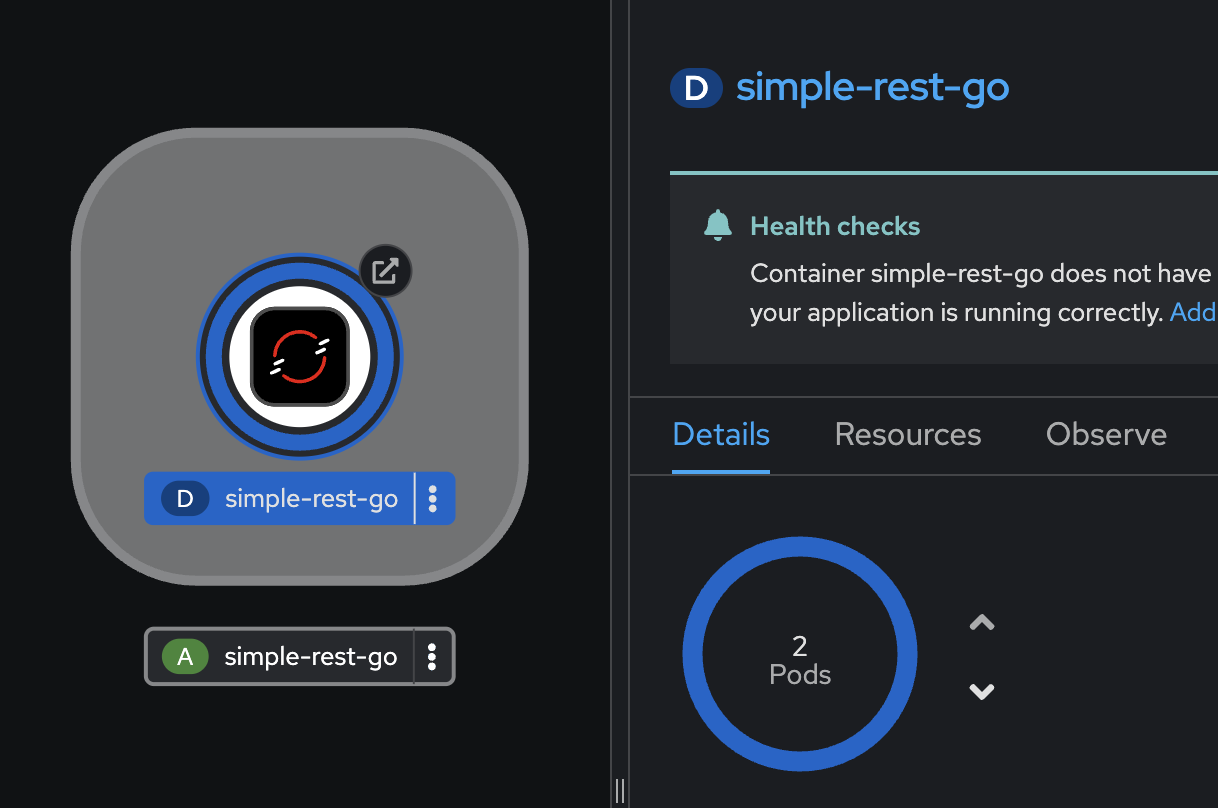
-
Go to Argo CD web console, on the Applications main page, you should see the status of
userX-go-prodapplication changed toOutOfSync. Click on the application tile to see details.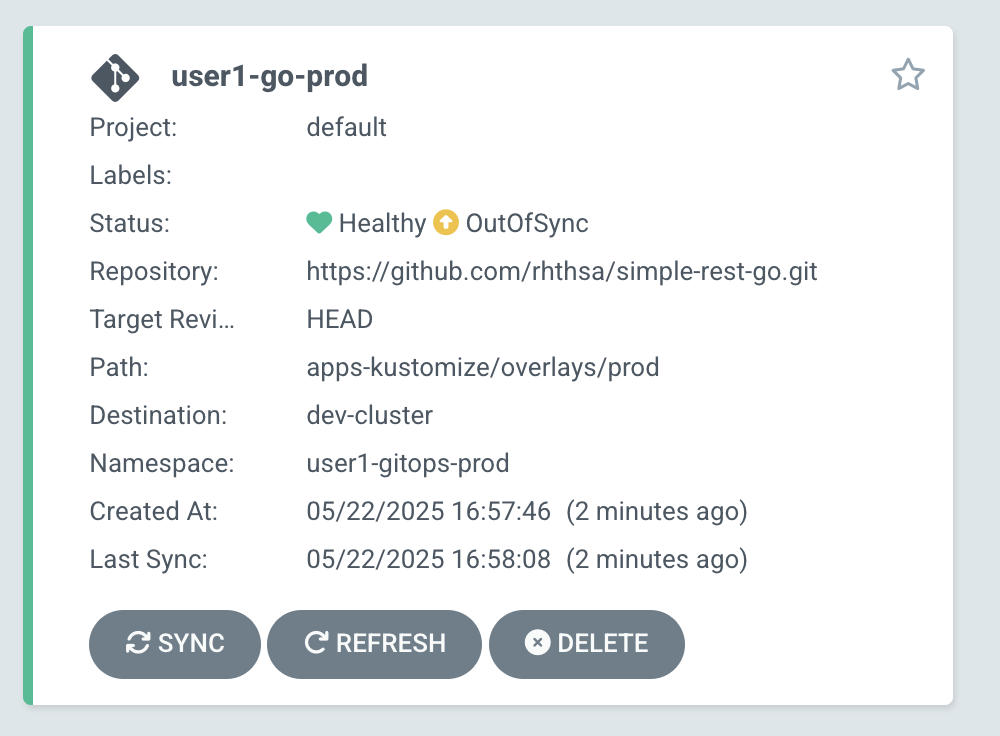
-
In the applicaiton details view, click on the DIFF button at the top.
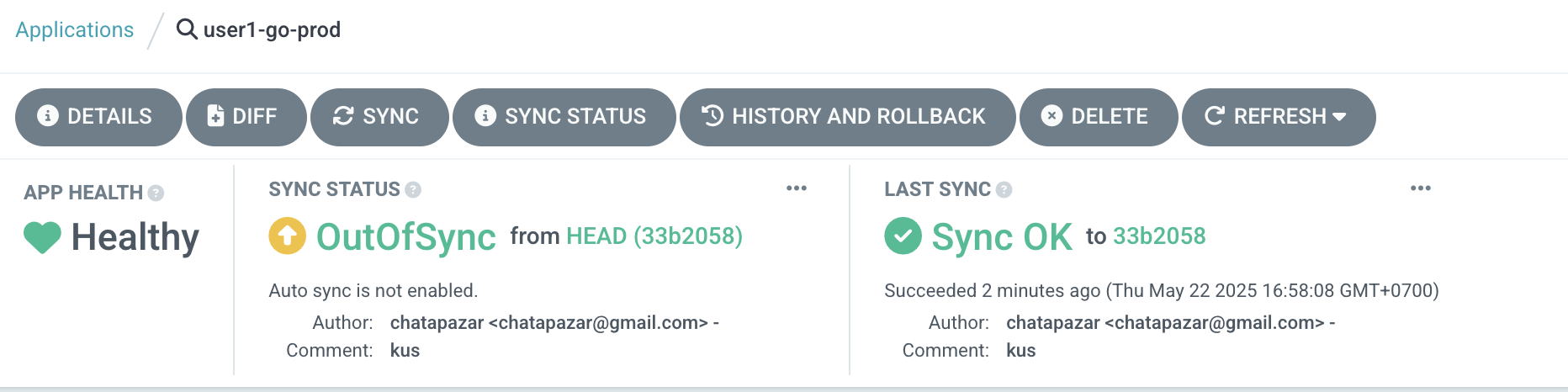
-
Select compact diff and inline diff checkbox to view the differences between current configuration in OpenShift cluster and the configurations file on Git.
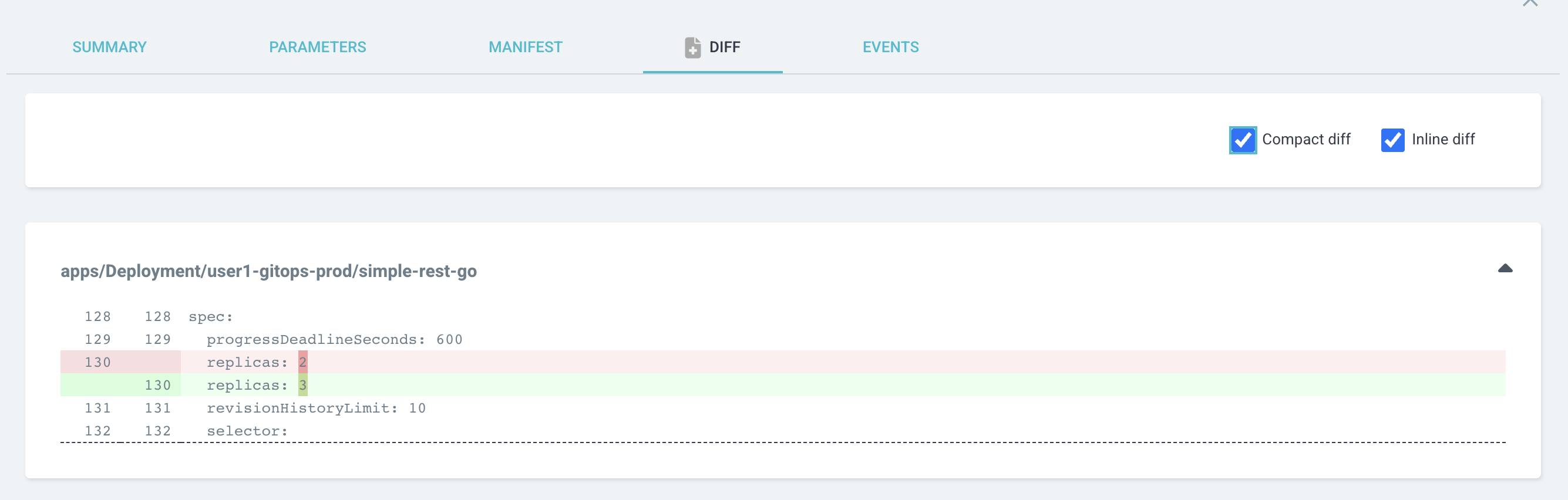
-
Click SYNC button, then click SYNCHRONIZE to synchronize configurations from Git to OpenShift again.
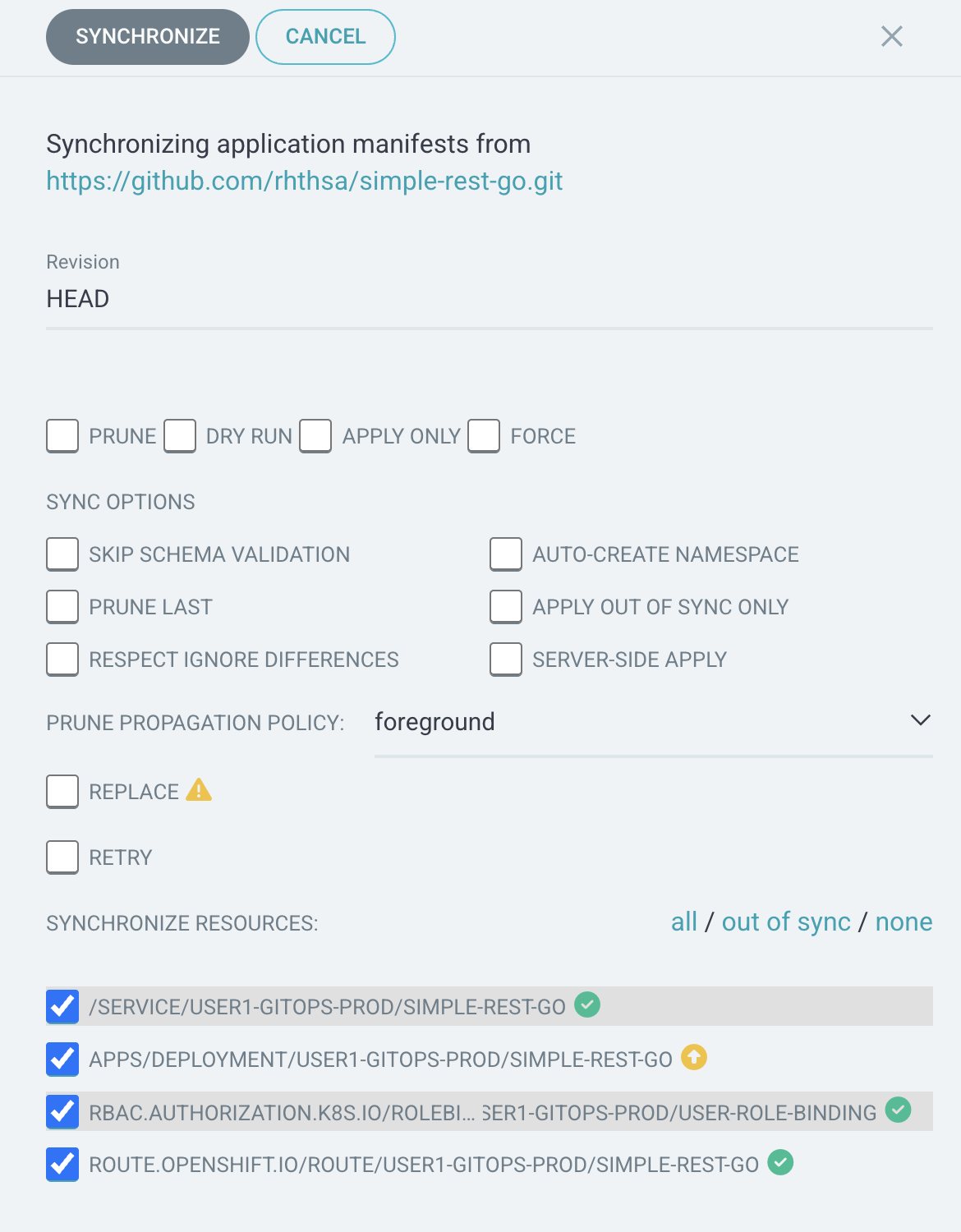
-
Go back to OpenShift console and check the number of replicas of
simple-rest-goDeployment again. It should be back to 3 replicas.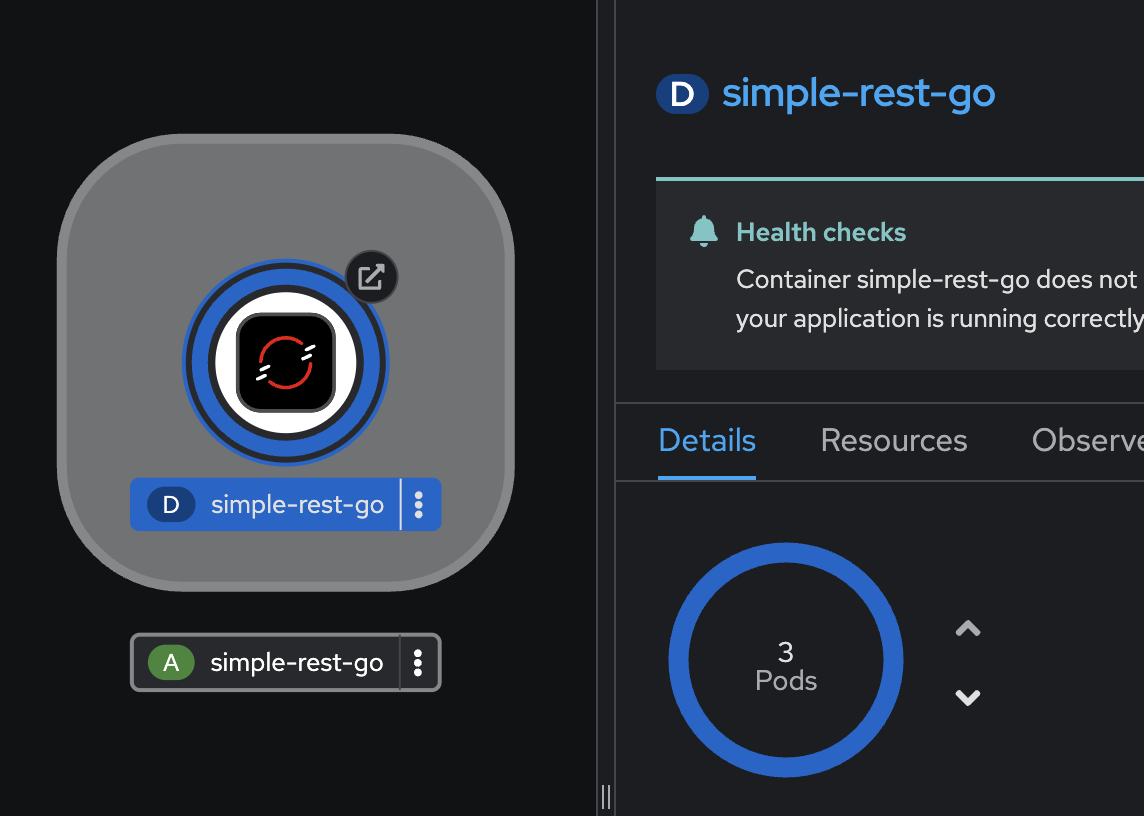
Summary
OpenShift GitOps takes advantage of Argo CD and integrates it into Red Hat OpenShift to deliver a consistent, fully supported, declarative Kubernetes platform to configure and use with GitOps principles.
OpenShift and OpenShift GitOps:
-
Apply consistency across cluster and deployment lifecycles
-
Consolidate administration and management of applications across on-premises and cloud environments
-
Check the state of clusters making application constraints known early
-
Rollback code changes across clusters
-
Roll out new changes submitted via Git
-
Support advanced deployment strategies, including blue green and canary, using automated traffic management and testing capabilities with Argo Rollouts.